Greater superficial petrosal nerve
| Greater petrosal nerve | |
|---|---|
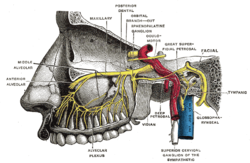
Alveolar branches of superior maxillary nerve and sphenopalatine ganglion.
|
|

Plan of the facial and intermediate nerves and their communication with other nerves.
|
|
| Details | |
| From | facial nerve |
| To | nerve of pterygoid canal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus petrosus major |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
n_05/12566464 |
| TA | A14.2.01.117 |
| FMA | 53417 |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
The greater (superficial) petrosal nerve (also known as the large superficial petrosal nerve) is a nerve in the skull that branches from the facial nerve; it forms part of a chain of nerves that innervate the lacrimal gland. The fibres have synapses in the pterygopalatine ganglion (also known as the sphenopalatine ganglion).
Preganglionic parasympathetic fibres arise in the superior salivary nucleus of the pontine tegmentum. They join with general somatic sensory and special sensory fibres to form the nervus intermedius. The nervus intermedius exits the cranial cavity at the Internal auditory meatus, and joins with the motor root of the facial nerve at the geniculate ganglion. While preganglionic parasympathetic fibres pass through the geniculate ganglion, they neither synapse, nor have their cell bodies located there.
Preganglionic parasympathetic fibres exit the geniculate ganglion as the greater petrosal nerve. It enters the middle cranial fossa through the hiatus of the facial canal, along with the petrosal branch of the middle meningeal artery. It enters the foramen lacerum, where it joins the deep petrosal nerve (a sympathetic nerve) to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal, which passes through the pterygoid canal to reach the pterygopalatine ganglion.
...
Wikipedia
