Google Cloud Messaging
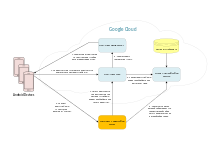
Overview of the GCM Service architecture.
|
|
| Developer(s) | |
|---|---|
| Target platform(s) | Android, Chrome |
| Programming language(s) | Java |
| Status | Active |
| License | Proprietary |
Google Cloud Messaging (commonly referred to as GCM) is a mobile notification service developed by Google that enables third-party application developers to send notification data or information from developer-run servers to applications that target the Google Android Operating System, as well as applications or extensions developed for the Google Chrome internet browser. It is available to developers free of charge. The GCM Service was first announced in June 2012 as a successor to Google's now-defunct Android Cloud to Device Messaging (C2DM) service, citing improvements to authentication and delivery, new API endpoints and messaging parameters, and the removal of limitations on API send-rates and message sizes. It has been superseded by Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM).
GCM first launched as Google's Android Cloud to Device Messaging (C2DM) service, first featured in Android 2.2 by Google.
The transition to Google Cloud Messaging was first announced when the Android service was unveiled on June 27, 2012, at Google I/O. Shortly after announcing the Google Cloud Messaging service, Google published documentation to guide application developers with migrating from the C2DM and onto the new service. Migrating to the service required SDK and code changes, as well as a release of an application update to the publish repository (such as Google Play) for downloading and updating.
The Chrome service was announced before Google I/O 2013 in a blog post titled 'Building efficient apps and extensions with push messaging.'
At I/O 2015, Google announced a new SDK and iOS support.
Google Cloud Messaging functions using server APIs and SDKs, both maintained by Google. The GCM has the ability to send push notifications, deep-linking commands, and application data. Larger messages can be sent with up to 4 KB of payload data.
...
Wikipedia
