Gluteus medius muscle
| Gluteus medius | |
|---|---|
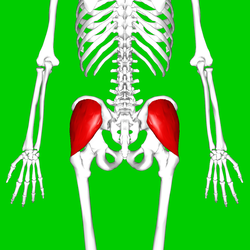
Position of gluteus medius muscle (shown in red). Posterior view.
|
|

The gluteus medius and nearby muscles.
|
|
| Details | |
| Origin | Gluteal surface of ilium, under gluteus maximus |
| Insertion | Greater trochanter of the femur |
| Artery | superior gluteal artery |
| Nerve | superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1 nerve roots) |
| Actions | abduction of the hip; preventing adduction of the hip. Medial rotation of thigh. |
| Antagonist | adductors |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus glutaeus medius |
| TA | A04.7.02.007 |
| FMA | 22315 |
|
Anatomical terms of muscle
[]
|
|
The gluteus medius (or glutæus medius), one of the three gluteal muscles, is a broad, thick, radiating muscle, situated on the outer surface of the pelvis.
Its posterior third is covered by the gluteus maximus, its anterior two-thirds by the gluteal aponeurosis, which separates it from the superficial fascia and integument.
The gluteus medius muscle starts, or "originates," on the outer surface of the ilium between the iliac crest and the posterior gluteal line above, and the anterior gluteal line below; the gluteus medius also originates from the gluteal aponeurosis that covers its outer surface.
The fibers of the muscle converge into a strong flattened tendon that inserts on the lateral surface of the greater trochanter. More specifically, the muscle's tendon inserts into an oblique ridge that runs downward and forward on the lateral surface of the greater trochanter.
A bursa separates the tendon of the muscle from the surface of the trochanter over which it glides.
The posterior border may be more or less closely united to the piriformis, or some of the fibers end on its tendon.
The posterior fibres of gluteus medius contract to produce hip extension, lateral rotation and abduction. During gait, the posterior fibres help to decelerate internal rotation of the femur at the end of swing phase.
With the leg in neutral position (straightened), the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus function together to pull the thigh away from midline, or "abduct" the thigh. During gait, these two muscles function principally in supporting the body on one leg, in conjunction with the tensor fasciae latae, to prevent the pelvis from dropping to the opposite side.
...
Wikipedia
