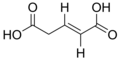
Glutaconic acid
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Pent-2-enedioic acid
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C5H6O4 | |||
| Molar mass | 130.099 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless solid | ||
| Melting point | 137 to 139 °C (279 to 282 °F; 410 to 412 K) | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
trans-Glutaconic acid is an organic compound with formula HO2CCH=CHCH2CO2H. This dicarboxylic acid exists as a colorless solid and is related to the saturated chemical glutaric acid, HO2CC(CH2)3CO2H. Esters and salts of glutaconic acid are called glutaconates.
The geometric isomer, cis-glutaconic acid, has a noticeably lower melting point (130–132 °C). It can be prepared by bromination of levulinic acid followed by treatment of the dibromoketone with potassium carbonate.
Glutaconic anhydride, which forms by dehydration the diacid, exists mainly as the dicarbonyl tautomer in solution. It is a colorless solid melting at 77–82 °C. Either the cis or trans diacid can be used to make it: the trans form isomerizes under the reaction conditions.
Glutaric, 3-hydroxglutaric, and glutaconic acids are structurally related metabolites. In Glutaric aciduria type 1, glutaconic acid accumulates, resulting in brain damage.
...
Wikipedia