Gliadorphin
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
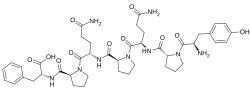
L-Tyrosyl-L-prolyl-L-glutaminyl-L-prolyl-L-glutaminyl-L-prolyl-L-phenylalanine
|
|
| Other names
Gluteomorphin; Gliadorphin-7
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C43H57N9O11 | |
| Molar mass | 875.98 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Gliadorphin (also known as gluteomorphin) is an opioid peptide that is formed during digestion of the gliadin component of the gluten protein. It is usually broken down into amino acids by digestion enzymes. It has been hypothesized that children with autism have abnormal leakage from the gut of this compound. This is partly the basis for the gluten-free, casein-free diet. Studies of this diet have had important methodological flaws, and the scientific evidence is not adequate to make treatment recommendations. However, abnormally high levels of gliadorphin have been found in the urine of autistic children via mass spectrometry testing.
...
Wikipedia
