Glia limitans
| Glial limiting membrane | |
|---|---|
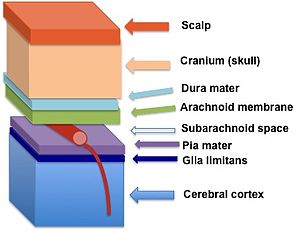
The glia limitans (in dark blue) lies between the pia mater and the cerebral cortex neurons
|
|
| Details | |
| Components | Astrocyte, Basal lamina |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Glia limitans |
| NeuroLex ID | Glia limitans |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
The glia limitans, or the glial limiting membrane, is a thin barrier of astrocyte foot processes associated with the parenchymal basal lamina surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost layer of neural tissue, and among its responsibilities is the prevention of the over migration of neurons and neuroglia, the supporting cells of the nervous system, into the meninges. The glia limitans also plays an important role in regulating the movement of small molecules and cells into the brain parenchyma by working in concert with other components of the central nervous system (CNS) such as the blood–brain barrier (BBB).
The end foot processes extending from both perivascular and marginal astrocytes form a close association with the basal lamina of the parenchyma, or the functional components of the brain, to create the glia limitans. This membrane lies deep to the pia mater and the subpial space and surrounds the perivascular (Virchow-Robin) spaces. Any substance entering the central nervous system from the blood or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) must cross the glia limitans.
The two different classifications of glial limiting membrane, the glia limitans perivascularis and the glia limitans superficialis, have nearly identical structures, however, they can be distinguished from each other by their location within the brain. The glia limitans perivascularis abuts the perivascular space surrounding the parenchymal blood vessels and functions as a supportive constituent of the blood–brain barrier. In contrast, the non-parenchymal blood vessels present in the subarachnoid space are not covered by the glia limitans. Instead, the entire subarachnoid space is sealed towards the nervous tissue by the glia limitans superficialis. These two parts of the glia limitans are continuous; however, convention dictates that the part that covers the surface of the brain is referred to as the superficialis, and the part that encloses the blood vessels within the brain is called the perivascularis.
...
Wikipedia
