Ghanaian presidential election, 2012
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
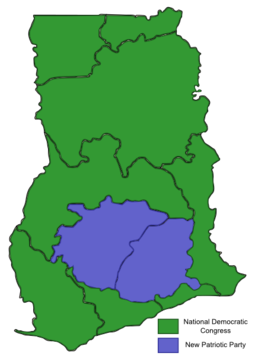
A general election was held in Ghana on Friday 7 December 2012 to elect a president and members of parliament in 275 electoral constituencies. Owing to the breakdown of some biometric verification machines, some voters could not vote, and voting was extended to Saturday 8 December 2012. A run-off was scheduled for 28 December 2012 if no presidential candidate received an absolute majority of 50% plus one vote. Competing for presidency were incumbent president John Dramani Mahama of the National Democratic Congress, his main challenger Nana Akufo-Addo of the New Patriotic Party and six other candidates.
Incumbent president John Mahama was declared winner of the election with 50.7% of the vote, just a few thousand votes over the threshold for avoiding a run-off election. Nana Akufo-Addo received 47.74%. The opposition alleged tampering with results by the Electoral Commission (EC), and filed a petition at the Ghanaian Supreme Court to review the election results. NPP produced more than 11,000 so-called "pink sheets" to the judges who had to compare them to similar papers from the EC, NDC and possibly other parties. These pink sheets state the results as counted in single polling stations, before aggregating them to any higher level, such as municipality, district and region. NPP claimed that there were differences between the results as stated immediately after their counting in polling stations, and those which were used in aggregations, and that this can be proven by the pink sheets. In a separate part of the procedure, the EC was challenged to prove that 14,000 expat Ghanaians had voted abroad, and failed to produce any registered voters in foreign countries due to, so EC, the fatal work of a virus in its computer.
Mahama was re-elected after less than five months as president having succeeded John Atta Mills who died suddenly in office in July 2012.
...
Wikipedia


