Germinal epithelium (male)
| Germinal epithelium (male) | |
|---|---|
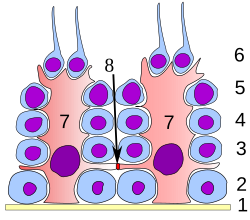
Germinal epithelium of the testicle. 1 basal lamina, 2 spermatogonia, 3 1st order, 4 spermatocyte 2nd order, 5 spermatid, 6 mature spermatid, 7 Sertoli cell, 8 tight junction (blood testis barrier)
|
|
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
e_13/12339107 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The germinal epithelium is the innermost layer of the testicle.
Germinal epithelium is also known as the wall of the seminiferous tubule within the testes. The cells in the epithelium are connected via tight junctions.
One may observe two types of cell in the germinal epithelium: The large Sertoli cells (which are not dividing) function as supportive cells to the developing sperm. The second cell type are the cells belonging to the spermatogenic cell lineage. These develop to eventually become sperm cells (Spermatozoon). Typically the spermatogenic cells will make four to eight layers in the germinal epithelium.
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
...
Wikipedia
