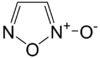
Furoxan
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
1,2,5-Oxadiazole 2-oxide
|
|
| Other names
Furazan N-oxide; Furazan 2-oxide
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | C528141 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C2H2N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 86.05 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Furoxan or 1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide is a heterocycle of the isoxazole family and an amine oxide derivative of furazan. It is a nitric oxide donor. As such, furoxan and its derivatives are actively researched as potential new drugs and insensitive high density explosives. Ipramidil is an example.
Furoxanes can be formed by dimerization of nitrile oxides.
...
Wikipedia
