Fort Hall
| Fort Hall | |
|---|---|
| Fur Trade Outpost | |
 |
|
| Constructed: | 1834 |
| Company built: | Nathaniel Jarvis Wyeth |
| Location: | Fort Hall, Idaho |
| Continent: | North America |
| Later Ownership: | 1837: Hudson's Bay Company, 1846: United States |
| Abandoned: | By 1863 |
|
Fort Hall
|
|

Marker at the first Fort Hall site, 1958
|
|
| Nearest city | Fort Hall, Idaho |
|---|---|
| Built | 1834 |
| NRHP Reference # | 66000306 |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | October 15, 1966 |
| Designated NHL | January 20, 1961 |
|
Fort Hall Site
|
|
| Nearest city | Fort Hall, Idaho |
|---|---|
| Built | 1870 |
| NRHP Reference # | 74000732 |
| Added to NRHP | November 21, 1974 |
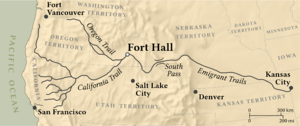
Fort Hall was built in 1834 as a fur trading post by Nathaniel Jarvis Wyeth on the Snake River in the eastern Oregon Country, part of southeastern Idaho in the present-day United States. He was an inventor and businessman from Boston, Massachusetts, who also founded a post at Fort William, in present-day Portland, Oregon, as part of a plan for a new trading and fisheries company. Unable to compete with the powerful British Hudson's Bay Company, based at Fort Vancouver, in 1837 Wyeth sold both posts to it. Great Britain and the United States both operated in the Oregon Country in these years.
After being included in United States territory in 1846 upon settlement of the northern boundary with Canada, Fort Hall developed as an important station for emigrants through the 1850s on the Oregon Trail; it was located at the end of the common 500-mile stretch from the East shared by the three far west emigrant trails. Soon after Fort Hall, the Oregon and California trails diverged in northwesterly and southwesterly directions. An estimated 270,000 emigrants reached Fort Hall on their way west. The town of Fort Hall, Idaho later developed 11 miles to the east, and Pocatello developed about 30 miles south on the Snake River.
In the 1860s, Fort Hall was the key post for the overland stage, mail and freight lines to the towns and camps of the mining frontier in the Pacific Northwest. In 1870 a New Fort Hall was constructed to carry out that function; it was located about 25 miles to the northeast. It protected stagecoach, mail and travelers to the Northwest.
Fort Hall is considered the most important trading post in the Snake River Valley. It was included within the Fort Hall Indian Reservation under the treaty of 1867. No building remains at either of its sites. The Old Fort Hall site was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1961, and the New Fort Hall site is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
...
Wikipedia


