Foramen Vesalii
| Sphenoidal emissary foramen | |
|---|---|
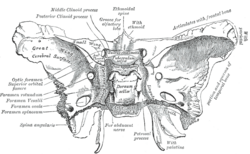
Sphenoid bone. Upper surface. (Sphenoidal emissary foramen labeled at left, fourth from bottom.)
|
|

Base of the skull. Upper surface. (Sphenoid is yellow, and sphenoidal emissary foramen is labeled at bottom of sphenoid.)
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Foramen venosum |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
f_12/12373813 |
| TA | A02.1.05.037 |
| FMA | 54785 |
|
Anatomical terms of bone
[]
|
|
In the base of the skull, in the great wings of the sphenoid bone, medial to the foramen ovale, a small aperture, the sphenoidal emissary foramen, may occasionally be seen (it is often absent) opposite the root of the pterygoid process. When present, it opens below near the scaphoid fossa. Vesalius was the first to describe and illustrate this foramen, and it thus sometimes bears the name of foramen Vesalii (meaning foramen of Vesalius). Other names include foramen venosum and canaliculus sphenoidalis.
If at all present, the sphenoidal emissary foramen gives passage to a small vein (vein of Vesalius) that connects the pterygoid plexus with the cavernous sinus. The importance of this passage lies in the fact that an infected thrombus from an extracranial source may reach the cavernous sinus. The mean area of the foramen is small, which may suggest that it plays a minor role in the dynamics of blood circulation in the venous system of the head.
The sphenoidal emissary foramen varies in size in different individuals, and is not always present on both sides of the sphenoid bone (one on each great wing of the sphenoid). In a study conducted under 100 skulls, the sphenoidal emissary foramen was only present in 17% of the cases, and it was always single.
In another study, the differences between the right and the left side as well as the differences between the male and the female sex were noted. Out of the 70 sides observed (35 skulls total), the sphenoidal emissary foramen was present in 32.85% of the cases (20.0% right side, 12.85% left side). The incidence of bilateral and unilateral sphenoidal emissary foramen was 22.85% (8 out of 35 skulls) and 20% (7 out of 35 skulls) respectively. Regarding the differences between the male and the female sex, no remarkable differences were observed, although the occurrence of the foramen was more in females compared to males (found in 13 sides in females and in 10 sides in males).
The skulls with one foramen were most frequent; those with two followed it and those with 3 (sphenoidal emissary) foramina were least frequent. Lang (1983) reported that the sphenoidal emissary foramen was present in about 40% of his material. It was found on the right side in 49% of the cases and in 36% of the cases on the left.
...
Wikipedia
