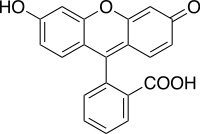
Fluorescein dye
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /fluːˈrɛsiᵻn/ or /fluːˈrɛsiːn/ |
|
IUPAC name
3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isobenzofuran-1(3H),9′-[9H]xanthen]-3-one
|
|
| Other names
Fluorescein, resorcinolphthalein, C.I. 45350, solvent yellow 94, D & C yellow no. 7, angiofluor, Japan yellow 201, soap yellow
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.302 |
| EC Number | 219-031-8 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Fluorescein |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C20H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 332.31 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.602 g/mL |
| Melting point | 314 to 316 °C (597 to 601 °F; 587 to 589 K) |
| Slightly | |
| Pharmacology | |
| S01JA01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | Warning |
| H319 | |
| P305, P351, P338 | |
| S-phrases | S26 S36 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Fluorescein is a manufactured organic compound and dye. It is available as a dark orange/red powder slightly soluble in water and alcohol. It is widely used as a fluorescent tracer for many applications.
Fluorescein is a fluorophore commonly used in microscopy, in a type of dye laser as the gain medium, in forensics and serology to detect latent blood stains, and in dye tracing. Fluorescein has an absorption maximum at 494 nm and emission maximum of 512 nm (in water). The major derivatives are fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and, in oligonucleotide synthesis, 6-FAM phosphoramidite.
The color of its aqueous solution varies from green to orange as a function of the way it is observed: by reflection or by transmission, as can be noticed in bubble levels, for example, in which fluorescein is added as a colorant to the alcohol filling the tube in order to increase the visibility of the air bubble contained within (thus enhancing the precision of the instrument). More concentrated solutions of fluorescein can even appear red.
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic health system.
...
Wikipedia
