Flat-headed cat
| Flat-headed Cat | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Genus: | Prionailurus |
| Species: | P. planiceps |
| Binomial name | |
|
Prionailurus planiceps (Vigors & Horsfield, 1827) |
|
 |
|
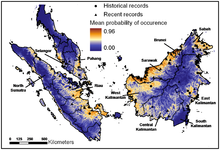
| Range of flat-headed cat | |
The flat-headed cat (Prionailurus planiceps) is a small wild cat patchily distributed in the Thai-Malay Peninsula, Borneo and Sumatra. Since 2008, it has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List due to destruction of wetlands in its habitat. It is suspected that the effective population size could be fewer than 2,500 mature individuals, with no subpopulation having an effective population size larger than 250 adult individuals.
Like some other small cats, it was originally placed in the genus Felis, but is now considered one of the five species in Prionailurus.
Flat-headed cats are very rare in captivity, with fewer than ten individuals, all kept in Malaysian and Thai zoos as recorded by ISIS.
The flat-headed cat is distinguished at once by the extreme depression of the skull, which extends along the nose to the extremity of the muzzle, the sides of which are laterally distended. The general habit of body is slender, and the extremities are delicate and lengthened. The head itself is more lengthened and cylindrical than in the domestic cat. The distance between the eyes and the ears is comparatively great. The cylindrical form and lateral contraction of the head is contrasted by an unusual length of the teeth. The canine teeth are nearly as long as in an individual of double its size.
The thick fur is reddish-brown on top of the head, dark roan brown on the body, and mottled white on the underbelly. The face is lighter in color than the body, and the muzzle and chin are white. Two prominent buff whitish streaks run on either side of the nose between the eyes. The ears are rounded. The eyes are unusually far forward and close together, compared with other cats, giving the felid improved stereoscopic vision. The teeth are adapted for gripping onto slippery prey, and the jaws are relatively powerful. These features help the flat-headed cat to catch and retain aquatic prey, to which it is at least as well adapted as the fishing cat. Legs are fairly short. Claws are retractable, but the covering sheaths are so reduced in size that about two-thirds of the claws are left protruding.
...
Wikipedia

