Flag of United States
 |
|
| Names | The American flag, The Stars and Stripes; Red, White and Blue; Old Glory; The Star-Spangled Banner |
|---|---|
| Use | National flag and ensign |
| Proportion | 10:19 |
| Adopted | June 14, 1777 (original 13-star version) July 4, 1960 (current 50-star version) |
| Design | Thirteen horizontal stripes alternating red and white; in the canton, 50 white stars of alternating numbers of six and five per row on a blue field |
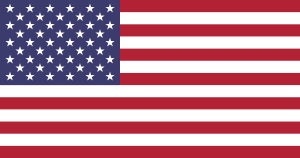
The flag of the United States of America, often referred to as the American flag, is the national flag of the United States. It consists of thirteen equal horizontal stripes of red (top and bottom) alternating with white, with a blue rectangle in the canton (referred to specifically as the "union") bearing fifty small, white, five-pointed stars arranged in nine offset horizontal rows, where rows of six stars (top and bottom) alternate with rows of five stars. The 50 stars on the flag represent the 50 states of the United States of America, and the 13 stripes represent the thirteen British colonies that declared independence from the Kingdom of Great Britain, and became the first states in the U.S. Nicknames for the flag include The Stars and Stripes,Old Glory, and The Star-Spangled Banner.
The current design of the U.S. flag is its 27th; the design of the flag has been modified officially 26 times since 1777. The 48-star flag was in effect for 47 years until the 49-star version became official on July 4, 1959. The 50-star flag was ordered by the then president Eisenhower on August 21, 1959, and was adopted in July 1960. It is the longest-used version of the U.S. flag and has been in use for over 56 years.
The Continental Colors
(aka the "Grand Union Flag")
Flag of the British East India Company, 1707–1801
At the time of the Declaration of Independence in July 1776, the Continental Congress would not legally adopt flags with "stars, white in a blue field" for another year. The flag contemporaneously known as "the Continental Colors" has historically been referred to as the first national flag.
The Continental Navy raised the Colors as the ensign of the fledgling nation in the American War for Independence—likely with the expedient of transforming their previous British red ensigns by adding white stripes—and would use this flag until 1777, when it would form the basis for the subsequent de jure designs.
...
Wikipedia
