Ferulate
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
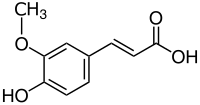
(E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)prop-2-enoic acid
|
|
| Other names
2-propenoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-
ferulic acid 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)acrylic acid 3-methoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid (2E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid Ferulate Coniferic acid trans-ferulic acid (E)-ferulic acid |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.173 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 194.18 g/mol |
| Appearance | Crystalline Powder |
| Melting point | 168 to 172 °C (334 to 342 °F; 441 to 445 K) |
| 0.78 g/L | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.61 |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Ferulic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, a type of organic compound. It is an abundant phenolic found in plant cell walls, covalently bonded as side chains to molecules such as arabinoxylans. As a component of lignin, ferulic acid is a precursor in the manufacture of other aromatic compounds. The name is derived from the genus Ferula, referring to the giant fennel (Ferula communis).
As a building block of lignocelluloses, such as pectin and lignin, ferulic acid is ubiquitous in the plant kingdom.
Ferulic acid is found in a number of vegetable sources, and occurs in particularly high concentrations in popcorn and bamboo shoots. It is a major metabolite of chlorogenic acids in humans along with caffeic and isoferulic acid, and is absorbed in the small intestine, whereas other metabolites such as dihydroferulic acid, feruloylglycine and dihydroferulic acid sulfate are produced from chlorogenic acid in the large intestine by the action of gut flora.
In cereals, ferulic acid is localized in the bran – the hard outer layer of grain. In wheat, phenolic compounds are mainly found in the form of insoluble bound ferulic acid and may be relevant to resistance to wheat fungal diseases. The highest known concentration of ferulic acid glucoside has been found in flaxseed (4.1 ± 0.2 g/kg). It is also found in barley grain.
Asterid eudicot plants can also produce ferulic acid. The tea brewed from the leaves of yacón (Smallanthus sonchifolius), a plant traditionally grown in the northern and central Andes, contains quantities of ferulic acid. In legumes, the white bean variety navy bean is the richest source of ferulic acid among the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) varieties. It is also found in horse grams (Macrotyloma uniflorum).
...
Wikipedia

