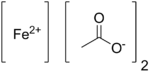
Ferrous acetate
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Iron(II) acetate
|
|
| Other names
Ferrous acetate
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3094-87-9 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider |
17323 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.492 |
| PubChem | 161387 |
| RTECS number | AI3850000 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C4H6FeO4 | |
| Molar mass | 173.93 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals (anhydrous) Light green crystals (tetrahydrate) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.734 g/cm3 (−73 °C) |
| Melting point | 190–200 °C (374–392 °F; 463–473 K) decomposes |
| Soluble | |
| Structure | |
| Orthorhombic, oP75 (200 K) | |
| Pbcn, No. 60 (200 K) | |
| 2/m 2/m 2/m (200 K) | |
|
a = 18.1715(4) Å, b = 22.1453(5) Å, c = 8.2781(2) Å (200 K)
α = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 90°
|
|
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P305+351+338 | |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26, S36 |
| NFPA 704 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Iron(II) acetate is an coordination complex with formula Fe(C2H3O2)2. It is a white solid, although impure samples can be slightly colored. A light green tetrahydrate is also known, which is highly soluble in water.
Iron powder reacts with hot acetic acid to give the product:
It adopts a polymeric structure with octahedral Fe(II) centers bridged by acetate ligands. It is not a salt.
The hydrate can be made by the reaction of ferrous oxide or ferrous hydroxide with acetic acid.
Reaction of scrap iron with acetic acid affords a brown mixture of various iron(II) and iron(III) acetates that are used in dyeing.
Ferrous acetate is used as a mordant by the dye industry. Ebonizing wood is one such process.
...
Wikipedia

