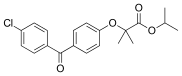
Fenofibrate
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Fenoglide, Lipofen |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601052 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | C10AB05 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Metabolism | glucuronidation |
| Biological half-life | 20 h |
| Excretion | urine (60%), feces (25%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
49562-28-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3339 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7186 |
| DrugBank |
DB01039 |
| ChemSpider |
3222 |
| UNII |
U202363UOS |
| KEGG |
D00565 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:5001 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL672 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.051.234 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H21ClO4 |
| Molar mass | 360.831 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Melting point | 80 to 81 °C (176 to 178 °F) |
|
|
|
|
Fenofibrate, marketed as Tricor and under several other brand names, is a drug of the fibrate class. It is mainly used to reduce cholesterol levels in people at risk of cardiovascular disease. Like other fibrates, it reduces both low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) levels, as well as increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels and reducing triglyceride levels. It is used alone or along with statins in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia.
Fenofibrate has been used since 1975 and is one of the most commonly prescribed fibrates.
Fenofibrate is mainly used for primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia. Fenofibrate appears to decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease and possibly diabetic retinopathy in those with diabetes mellitus, and firstly indicated for the reduction in the progression of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes and existing diabetic retinopathy in Australia. It also appears to be helpful in decreasing amputations of the lower legs in this same group of people. Fenofibrate also has an off-label use as an added therapy of high blood uric acid levels in people who have gout.
It is used in addition to diet to reduce elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL), total cholesterol, triglycerides (TG), and apolipoprotein B (apo B), and to increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) in adults with primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia.
...
Wikipedia
