External obturator
| External obturator muscle | |
|---|---|
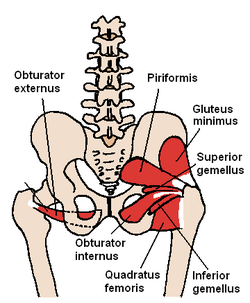
The obturator externus and nearby hip muscles (posterior view)
|
|

The Obturator externus. Anterior-Inferior view
|
|
| Details | |
| Origin | obturator foramen and obturator membrane |
| Insertion | trochanteric fossa of femur |
| Artery | obturator artery |
| Nerve | posterior branch of obturator nerve (third and fourth lumbar nerves) |
| Actions | adduct thigh, Laterally rotates thigh |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus obturatorius externus |
| TA | A04.7.02.031 |
| FMA | 22299 |
|
Anatomical terms of muscle
[]
|
|
The external obturator muscle, obturator externus muscle (/ˌɒbtjʊəˈreɪtər
It is sometimes considered part of the medial compartment of thigh, and sometimes considered part of the gluteal region.
It arises from the margin of bone immediately around the medial side of the obturator membrane and surrounding bone, viz., from the inferior pubic ramus, and the ramus of the ischium; it also arises from the medial two-thirds of the outer surface of the obturator membrane, and from the tendinous arch which completes the canal for the passage of the obturator vessels and nerves.
The fibers springing from the pubic arch extend on to the inner surface of the bone, where they obtain a narrow origin between the margin of the foramen and the attachment of the obturator membrane.
The fibers converge and pass posterolateral and upward, and end in a tendon which runs across the back of the neck of the femur and lower part of the capsule of the hip joint and is inserted into the trochanteric fossa of the femur.
The obturator vessels lie between the muscle and the obturator membrane; the anterior branch of the obturator nerve reaches the thigh by passing in front of the muscle, and the posterior branch by piercing it.
...
Wikipedia
