Event monitor
| Cardiac monitoring | |
|---|---|
| Medical diagnostics | |
|
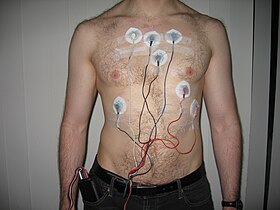
Cardiac monitoring generally refers to continuous monitoring of heart activity, generally by electrocardiography, with assessment of the patient's condition relative to their cardiac rhythm. It is different from hemodynamic monitoring, which monitors the pressure and flow of blood within the cardiovascular system. The two may be performed simultaneously on critical heart patients. A small monitor worn by an ambulatory patient (one well enough to walk around) is known as a Holter monitor. Transmitting data from a monitor to a distant monitoring station is known as telemetry or biotelemetry.
In the setting of out-of-hospital acute medical care, ambulance services and other emergency medical services providers utilize heart monitors to assess the patient's cardiac rhythm. Providers licensed or certified at the Intermediate or Paramedic level are qualified to interpret ECGs. The finding of a cardiac dysrhythmia (or for that matter, a normal sinus rhythm) may give additional information about the patient's condition or may be a sufficient diagnosis on its own to guide treatment. Treatment for specific cardiac rhythms is guided by ACLS. Basic EMTs are allowed to apply the electrodes and physically operate the monitor but not interpret the rhythm.
In the emergency department, cardiac monitoring is a part of the monitoring of vital signs in emergency medicine, and generally includes electrocardiography.
...
Wikipedia
