Eugenol
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
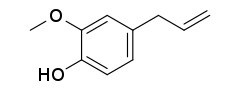
2-Methoxy-4-(prop-2-en-1-yl)phenol
|
|
| Other names
4-Allyl-2-methoxyphenol
2-Methoxy-4-(2-propenyl)phenol Eugenic acid Caryophyllic acid 1-Allyl-3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzene Allylguaiacol 2-Methoxy-4-allylphenol 4-Allylcatechol-2-methyl ether |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.355 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 164.20 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.06 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −7.5 °C (18.5 °F; 265.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 254 °C (489 °F; 527 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.19 at 25 °C |
| -102.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 104 °C (219 °F; 377 K) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
2-Phenethyl propionate |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Eugenol /juːdʒɪnɒl/ is a phenylpropene, an allyl chain-substituted guaiacol. Eugenol is a member of the phenylpropanoids class of chemical compounds. It is a colourless to pale yellow, aromatic oily liquid extracted from certain essential oils especially from clove oil, nutmeg, cinnamon, basil and bay leaf. It is present in concentrations of 80–90% in clove bud oil and at 82–88% in clove leaf oil.
Eugenol is used in perfumes, flavorings, and essential oils. It is also used as a local antiseptic and anaesthetic. Eugenol can be combined with zinc oxide to form zinc oxide eugenol which has restorative and prosthodontic applications in dentistry. For example, zinc oxide eugenol is used for root canal sealing.
Attempts have been made to develop eugenol derivatives as intravenous anesthetics, as an alternative to propanidid which produces unacceptable side effects around the site of injection in many patients.
It can be used to reduce the presence of Listeria monocytogenes and Lactobacillus sakei in food.
It is also used in manufacturing stabilizers and antioxidants for plastics and rubbers.
...
Wikipedia

