Estradiol (medication)
 |
|||
|
|||
| Clinical data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌɛstrəˈdaɪoʊl/ ES-trə-DYE-ohl | ||
| Trade names | Numerous | ||
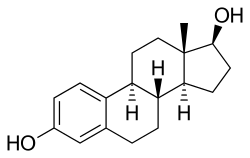
| Synonyms | 17β-Estradiol; Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol | ||
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph | ||
| Pregnancy category |
|
||
| Routes of administration |
• By mouth (tablet) • Sublingual (tablet) • Intranasal (nasal spray) • Topical (gel, cream, patch, spray, emulsion) • Vaginal (tablet, cream, ring) • I.M. injection (oil solution) • S.C. injection (aq. soln.) • Subcutaneous implant |
||
| ATC code | |||
| Legal status | |||
| Legal status | |||
| Pharmacokinetic data | |||
| Bioavailability | Oral: <5% | ||
| Protein binding | ~98%: • Albumin: 60% • SHBG: 38% • Free: 2% |
||
| Metabolism | Liver (via hydroxylation, sulfation, glucuronidation) | ||
| Metabolites | Major (90%): • Estrone • Estrone sulfate • Estrone glucuronide • Estradiol glucuronide |
||
| Biological half-life | Oral: 13–20 hours Sublingual: 8–18 hours Topical (gel): 36.5 hours |
||
| Excretion |
Urine: 54% Feces: 6% |
||
| Identifiers | |||
|
|||
| CAS Number | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| IUPHAR/BPS | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| UNII | |||
| KEGG | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| Chemical and physical data | |||
| Formula | C18H24O2 | ||
| Molar mass | 272.38 g/mol | ||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
|
|||
|
|||
Estradiol, also spelled oestradiol, is a medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is an estrogen and is used mainly in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for menopause,hypogonadism, and transgender women. It is also used in hormonal contraception and sometimes in the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers like prostate cancer. Estradiol can be taken by mouth, as a gel or patch that is applied to the skin, in through the vagina, by injection into muscle, or through the use of an implant that is placed into fat, among other routes.
Side effects of estradiol in women include breast tenderness and enlargement, headache, fluid retention, and nausea. Men and children who are exposed to estradiol may develop symptoms of feminization, such as breast development, and men may also experience hypogonadism and infertility. It may increase the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer in women with an intact uterus if it is not taken together with a progestogen like progesterone. Estradiol should not be used in women who are pregnant or breastfeeding or who have breast cancer.
...
Wikipedia