Erect penis
| Erection | |
|---|---|
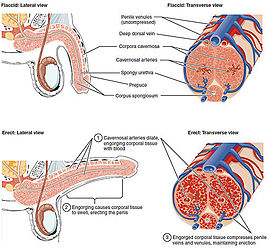
Three columns of erectile tissue make up most of the volume of the penis.
|
|
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firmer, engorged and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular and endocrine factors, and is often associated with sexual arousal or sexual attraction, although erections can also be spontaneous. The shape, angle and direction of an erection varies considerably in humans.
Physiologically, erection is triggered by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), causing nitric oxide (a vasodilator) levels to rise in the trabecular arteries and smooth muscle of the penis. The arteries dilate causing the corpora cavernosa of the penis (and to a lesser extent the corpora spongiosum) to fill with blood; simultaneously the ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles compress the veins of the corpora cavernosa restricting the egress and circulation of this blood. Erection subsides when parasympathetic activity reduces to baseline.
As an autonomic nervous system response, an erection may result from a variety of stimuli, including sexual stimulation and sexual arousal, and is therefore not entirely under conscious control. Erections during sleep or upon waking up are known as nocturnal penile tumescence (NPT). Absence of nocturnal erection is commonly used to distinguish between physical and psychological causes of erectile dysfunction and impotence.
...
Wikipedia
