Epoöphoron
| Epoophoron | |
|---|---|
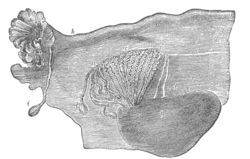
Broad ligament of adult, showing epoöphoron. (From Farre, after Kobelt.) a, a. Epoöphoron formed from the upper part of the Mesonephric body. b. Remains of the uppermost tubes sometimes forming appendices. c. Middle set of tubes. d. Some lower atrophied tubes. e. Atrophied remains of the Mesonephric duct. f. The terminal bulb or hydatid. h. The uterine tube, originally the duct of Müller. i. Appendix attached to the extremity. l. The ovary.
|
|

Uterus and right broad ligament, seen from behind. The epoophoron is visible in upper right
|
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | mesonephric duct |
| Identifiers | |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
e_13/12339465 |
| TA | A09.1.05.001 |
| FMA | 18691 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The epoophoron or epoöphoron (also called organ of Rosenmüller or the parovarium) is a remnant of the mesonephric tubules that can be found next to the ovary and fallopian tube.
It may contain 10–15 transverse small ducts or tubules that lead to the Gartner’s duct (also longitudinal duct of epoophoron) that represents the caudal remnant of the Mesonephric duct and passes through the broad ligament and the lateral wall of the cervix and vagina.
The epoophoron is a homologue to the epididymis in the male.
While the epoophoron is located in the lateral portion of the mesosalpinx and mesovarium, the paroophoron (residual remnant of that part of the Mesonephric duct that forms the paradidymis in the male) lies more medially in the mesosalpinx.
It has a unique histological profile.
Clinically the organ may give rise to a local paraovarian cyst or adenoma.
...
Wikipedia
