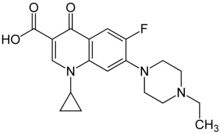
Enrofloxacin
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral, subcutaneous injection, topical (ear drops) |
| ATCvet code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80% in dogs, 65-75% in sheep |
| Metabolism | Renal and non-renal |
| Biological half-life | 4–5 hours in dogs, 6 hours in cats, 1.5 - 4.5 hours in sheep. |
| Excretion | Bile (70%); Renal (30%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.131.355 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H22FN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 359.4 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Enrofloxacin (ENR) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic sold by the Bayer Corporation under the trade name Baytril. Enrofloxacin is currently approved by the FDA for the treatment of individual pets and domestic animals in the United States. In September 2005, the FDA withdrew approval of Baytril for use in water to treat flocks of poultry, as this practice was noted to promote the evolution of fluoroquinolone-resistant strains of the bacterium Campylobacter, a human pathogen.
It is a bactericidal agent. The bactericidal activity of enrofloxacin is concentration-dependent, with susceptible bacteria cell death occurring within 20–30 minutes of exposure. Enrofloxacin has demonstrated a significant post-antibiotic effect for both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and is active in both stationary and growth phases of bacterial replication. Enrofloxacin is partially deethylated by CYP450 into the active metabolite ciprofloxacin, which is also a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, used preferentially in humans.
Enrofloxacin is a synthetic antibacterial agent from the class of the fluoroquinolone carboxylic acid derivatives. It has antibacterial activity against a broad spectrum of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Its mechanism of action is not thoroughly understood, but it is believed to act by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase (a type-II topoisomerase), thereby preventing DNA supercoiling and DNA synthesis. It is effective against:
Variable activity against:
Ineffective against:
The following data represent minimum inhibitory concentration ranges for a few medically significant bacterial pathogens:
Usage in poultry.
Enrofloxacin was banned for poultry use in 2005. Baytril should not be used in rapidly growing animals (for example dogs under 12 months - 18 months in large breeds, or kittens under 8 weeks) as it causes abnormalities in the development of articular cartilage.
...
Wikipedia
