English East India Company

Company flag (1801)
|
|

Coat of arms (1698)
|
|
| Industry | International trade |
|---|---|
| Fate | Dissolved |
| Founded | 31 December 1600 |
| Founders | John Watts, George White |
| Defunct | 1 June 1874 |
| Headquarters | London, England |
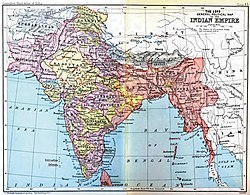
Imperial entities of India
|
|
| Dutch India | 1605–1825 |
|---|---|
| Danish India | 1620–1869 |
| French India | 1769–1954 |
|
|
|
| Casa da Índia | 1434–1833 |
| Portuguese East India Company | 1628–1633 |
|
|
|
| East India Company | 1612–1757 |
| Company rule in India | 1757–1858 |
| British Raj | 1858–1947 |
| British rule in Burma | 1824–1948 |
| Princely states | 1721–1949 |
| Partition of India |
1947
|
|
|
|
The East India Company (EIC), also known as the Honourable East India Company (HEIC) or the British East India Company and informally as John Company, was an English and later British , which was formed to pursue trade with the East Indies but ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and Qing China.
Originally chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London trading into the East Indies", the company rose to account for half of the world's trade, particularly in basic commodities including cotton, silk, indigo dye, salt, saltpetre, tea and opium. The company also ruled the beginnings of the British Empire in India.
The company received a Royal Charter from Queen Elizabeth I on 31 December 1600, making it the oldest among several similarly formed European . Wealthy merchants and owned the Company's shares. The government owned no shares and had only indirect control.
The company eventually came to rule large areas of India with its own private armies, exercising military power and assuming administrative functions.Company rule in India effectively began in 1757 after the Battle of Plassey and lasted until 1858 when, following the Indian Rebellion of 1857, the Government of India Act 1858 led to the British Crown assuming direct control of India in the form of the new British Raj.
Despite frequent government intervention, the company had recurring problems with its finances. It was dissolved in 1874 as a result of the passed one year earlier, as the Government of India Act had by then rendered it vestigial, powerless, and obsolete. The official government machinery of British India had assumed its governmental functions and absorbed its armies.
...
Wikipedia
