Endocrine glands
| Endocrine glands | |
|---|---|
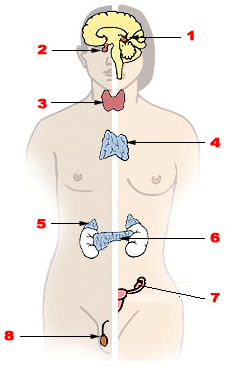
The major endocrine glands:
1 Pineal gland 2 Pituitary gland 3 Thyroid gland 4 Thymus 5 Adrenal gland 6 Pancreas 7 Ovary (female) 8 Testis (male) |
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | glandulae endocrinae |
| Code | TH H2.00.02.0.03072 |
| TA | 11.0.00.000 |
| FMA | 71653 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
1 Pineal gland 2 Pituitary gland 3 Thyroid gland 4 Thymus 5 Adrenal gland 6 Pancreas 7 Ovary (female)
Endocrine glands are glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood rather than through a duct. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are neuroendocrine organs. Local chemical messengers, not generally considered part of the endocrine system, include , which act on the cells that secrete them, and paracrines, which act on a different cell type nearby.
The ability of a target cell to respond to a hormone depends on the presence of receptors, within the cell or on its plasma membrane, to which the hormone can bind.
Hormone receptors are dynamic structures. Changes in number and sensitivity of hormone receptors may occur in response to high or low levels of stimulating hormones.
Blood levels of hormones reflect a balance between secretion and degradation/excretion. The liver and kidneys are the major organs that degrade hormones; breakdown products are excreted in urine and feces.
...
Wikipedia
