Elephantomyia baltica
|
Elephantomyia baltica Temporal range: Middle Eocene |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
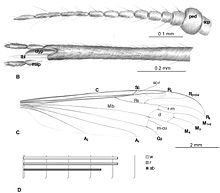
| illustrations of E. (E.) baltica anatomy | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Diptera |
| Family: | Limoniidae |
| Genus: | Elephantomyia |
| Species: | †E. baltica |
| Binomial name | |
|
Elephantomyia baltica Alexander, 1931 |
|
Elephantomyia (Elephantomyia) baltica is an extinct species of crane fly in the family Limoniidae. The species is solely known from the Middle EoceneBaltic amber deposits in the Baltic Sea region of Europe. The species is one of six described from Baltic amber.
Elephantomyia (Elephantomyia) baltica is known from the holotype specimen, collection number 282, a solitary complete adult which has been preserved as an inclusion in transparent Baltic amber. As of 2015, the amber specimen, number 282, was included in the collections of the University of Göttingen. Baltic amber is recovered from fossil bearing rocks in the Baltic Sea region of Europe. Estimates of the age date between 37 million years old, for the youngest sediments and 48 million years old. This age range straddles the middle Eocene, ranging from near the beginning of the Lutetian to the beginning of the Pribonian. E. baltica is one of six crane fly species in the genus Elephantomyia described from the Baltic amber, the others being E. brevipalpa, E. bozenae, E. irinae, E. longirostris, and E. pulchella. All six species are placed into the Elephantomyia subgenus Elephantomyia based on the lack of tibial spurs and by several aspects of the wing morphology.
The fossil was first studied by entomologist Charles Paul Alexander of the Massachusetts Agricultural College, with his 1931 type description of the new species being published in his monograph Crane flies of the Baltic Amber (Diptera). The fossil was reexamined and the species redescribed in 2015 by paleoentomologist Iwona Kania of the University of Rzeszów.
...
Wikipedia
