Dysdera crocata
| Woodlouse spider | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Suborder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Dysderidae |
| Genus: | Dysdera |
| Species: | D. crocata |
| Binomial name | |
|
Dysdera crocata C. L. Koch, 1838 |
|
 |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
The woodlouse spider, Dysdera crocata, is a species of spider that preys primarily upon woodlice. Other common names refer to variations on the common name of its prey, including woodlouse hunter, sowbug hunter, sowbug killer, pillbug hunter and slater spider.
Female specimens are 15–30 mm long, while males are 10–15 mm. They have six eyes, a dark-red cephalothorax and legs, and a shiny (sometimes very shiny) yellow-brown abdomen. Notably, they have disproportionately large chelicerae for a spider of this size. Dysdera crocata is difficult to distinguish from the much less common Dysdera erythrina though this species is not often found near human habitation.
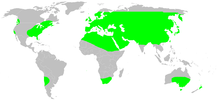
D. crocata, which originated in the Mediterranean area, now has a cosmopolitan distribution (see map), ranging from Eurasia to parts of North and South America, South Africa, Australia, and New Zealand.
Woodlouse spiders are usually found under logs, rocks, bricks, and in leaf litter in warm places, often close to woodlice. They have also been found in houses. They spend the day in a silken retreat made to enclose crevices in, generally, partially decayed wood, but sometimes construct tent-like structures in indents of various large rocks. Woodlouse spiders hunt at night and do not spin webs.
Their diet consists principally of woodlice which—despite their tough exoskeleton—are pierced easily by the spider's large chelicerae; the spider usually stabs and injects venom into the woodlouse's soft underbelly while avoiding any noxious defensive chemicals. Laboratory experiments have shown D. crocata will take other invertebrates, and shows no particular preference for woodlice; these are simply the most common prey in its habitat. Other invertebrates preyed on by D. crocata include silverfish, earwigs, millipedes, and small burying beetles. This small but huge-fanged spider is very well equipped to prey on underground invertebrates of almost any kind.
...
Wikipedia
