Dwarf Crocodile
| Dwarf crocodile | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Dwarf crocodile | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Subphylum: | Vertebrata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Crocodilia |
| Family: | Crocodylidae |
| Genus: |
Osteolaemus Cope, 1861 |
| Species: | O. tetraspis |
| Binomial name | |
|
Osteolaemus tetraspis Cope, 1861 |
|
| Subspecies | |
|
|
 |
|
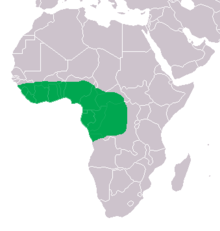
| Range of the dwarf crocodile in green | |
The dwarf crocodile (Osteolaemus tetraspis), also known commonly as the African dwarf crocodile, broad-snouted crocodile, or bony crocodile, is an African crocodile that is also the smallest extant crocodile species. Recent sampling has identified three genetically distinct populations. Some feel that the findings should elevate the subspecies to full species status.
Osteolaemus tetraspis is currently the only species included in the genus Osteolaemus, with two recognized subspecies:
The second subspecies has had a somewhat convoluted taxonomical history. It was first described as Osteoblepharon osborni by Schmidt in 1919, based on a few specimens from the Upper Congo Basin in what is now the Democratic Republic of Congo. However, Inger in a 1948 paper found the specimens wanting of characteristics that would justify a generic separation from Osteolaemus and referred the specimens to Osteolaemus osborni. Later, Wermuth and Mertens (1961), reduced it to the current subspecies rank.
Recent evidence from the analysis of DNA indicates that three distinctly different populations of Osteolaemus may merit full species recognition. These would be O. tetrapis, O. osborni, and a third currently unnamed species.
The generic name, Osteolaemus, means "bony throat", and is derived from the Ancient Greek όστεον (bone) and λαιμός (throat). The genus was named as such due to the osteoderms found among the scales in the neck and belly.
The specific epithet, tetraspis, means "four shields", and derives from the Ancient Greek τετρα (four) and ασπίς (shield), as the back of the neck has four large, shield-like scales.
...
Wikipedia

