Drupal
 |
|
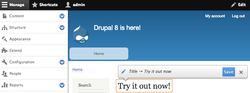
Drupal 8 in action. Showing in-context editing and previews (WYSIWYG).
|
|
| Original author(s) | Dries Buytaert |
|---|---|
| Initial release | May 18, 2000 |
| Stable release |
8.2.6 / 1 February 2017
|
| Repository | cgit |
| Development status | Active |
| Written in | PHP, using Symfony |
| Operating system | Unix-like, Windows |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Size | 80 MB (uncompressed Drupal 8 core) |
| Available in | Multilingual |
| Type | Content management framework, Content management system, Community and Blog software |
| License | GPLv2 or later |
| Website | www |
Drupal /ˈdruːpəl/, a free and open source content-management framework written in PHP and distributed under the GNU General Public License, provides a back-end framework for at least 2.2% of all Web sites worldwide – ranging from personal blogs to corporate, political, and government sites. Systems also use Drupal for knowledge management and for business collaboration.
The standard release of Drupal, known as Drupal core, contains basic features common to content-management systems. These include user account registration and maintenance, menu management, RSS feeds, taxonomy, page layout customization, and system administration. The Drupal core installation can serve as a simple Web site, a single- or multi-user blog, an Internet forum, or a community Web site providing for user-generated content.
"The Drupal Overview", a feature of the project web site, describes it as a content management framework. Drupal also describes itself as a Web application framework, as it meets the generally acceptedfeature requirements for such frameworks.
As of January 2017[update] the Drupal community is composed of more than one million members. Including 105,400 users actively contributing. Resulting in more than 35,800 free modules that extend and customize Drupal functionality, over 2,300 free themes that change the look and feel of Drupal, and at least 1,100 free distributions that allow you to quickly and easily set up a complex, use-specific Drupal in fewer steps.
...
Wikipedia
