Donepezil
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Aricept |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a697032 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | N06DA02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 100% |
| Protein binding | 96% |
| Biological half-life | 70 hours |
| Excretion | 0,11-0,13 (l/h/kg) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
120014-06-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3152 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 6599 |
| DrugBank |
DB00843 |
| ChemSpider |
3040 |
| UNII |
8SSC91326P |
| KEGG |
D07869 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:53289 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL502 |
| PDB ligand ID | E20 (PDBe, RCSB PDB) |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.125.198 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
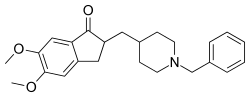
| Formula | C24H29NO3 |
| Molar mass | 379.492 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
|
|
|
|
Donepezil, marketed under the trade name Aricept, is a medication used in the palliative treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Donepezil is used to improve cognition and behavior of people with Alzheimer's, but does not slow the progression of or cure the disease.
Common side effects include loss of appetite, gastrointestinal upset, diarrhea, difficulty sleeping, vomiting, or muscle cramping.
It was developed by Eisai and Pfizer and is sold as a generic by multiple suppliers. Donepezil acts as a centrally acting reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.
There is no evidence that donepezil or other similar agents alters the course or progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). 6 to 12-month controlled studies have shown modest benefits in cognition and/or behavior. The UK National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) recommends donepezil as an option in the management of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. The person should, however, be reviewed frequently and if there is no significant benefit it should be stopped. In 2006 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration also approved donepezil for treatment of mild, moderate and severe dementia in Alzheimer's disease.
In clinical trials the most common adverse events leading to discontinuation were nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting. Other side effects included difficulty sleeping, muscle cramps and anorexia. Most side effects were observed in patients taking the 23 mg dose compared to 10 mg or lower doses. Side effects improved with continued use.
Donepezil should be used with caution in people with heart disease, cardiac conduction disturbances, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, severe cardiac arrhythmias and sick sinus syndrome.
...
Wikipedia
