Diphtheria toxin
| Diphtheria toxin, C domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
complex of diphtheria toxin and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Diphtheria_C | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF02763 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0084 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR022406 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1ddt | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1ddt | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.C.7 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
| Diphtheria toxin, T domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

complex of diphtheria toxin and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Diphtheria_T | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF02764 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR022405 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1ddt | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1ddt | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.C.7 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
| Diphtheria toxin, R domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

complex of diphtheria toxin and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Diphtheria_R | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01324 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR022404 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1ddt | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1ddt | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.C.7 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
| tox diphtheria toxin precursor | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Organism | |
| Symbol | tox |
| Entrez | 2650491 |
| RefSeq (Prot) | NP_938615 |
| UniProt | Q6NK15 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 2.4.2.36 |
| Chromosome | genome: 0.19 - 0.19 Mb |
Diphtheria toxin is an exotoxin secreted by Corynebacterium diphtheriae, the pathogenic bacterium that causes diphtheria. Unusually, the toxin gene is encoded by a bacteriophage (a virus that infects bacteria). The toxin causes the disease diphtheria in humans by gaining entry into the cell cytoplasm and inhibiting protein synthesis.
Diphtheria toxin is a single polypeptide chain of 535 amino acids consisting of two subunits linked by disulfide bridges, known as an A-B toxin. Binding to the cell surface of the B subunit (the less stable of the two subunits) allows the A subunit (the more stable part of the protein) to penetrate the host cell.
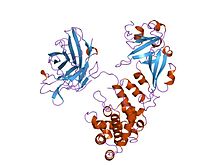
The crystal structure of the diphtheria toxin homodimer has been determined to 2.5 Ångstrom resolution. The structure reveals a Y-shaped molecule consisting of three domains. Fragment A contains the catalytic C domain, and fragment B consists of the T and R domains:
The diphtheria toxin has the same mechanism of action as the enzyme NAD(+)—diphthamide ADP-ribosyltransferase (EC 2.4.2.36). It catalyzes the transfer of NAD+ to a diphthamide residue in eEF-2, inactivating this protein. It does so by ADP-ribosylating the unusual amino acid diphthamide. In this way, it acts as a RNA translational inhibitor. The catalysed reaction is as follows:
...
Wikipedia
