Digenean
| Digenea | |
|---|---|
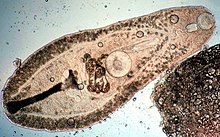 |
|
| Helicometra sp. (Plagiorchiida: Opecoelidae) from the intestine of a Flame Cardinal fish | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Trematoda |
| Subclass: |
Digenea Carus, 1863 |
| Families | |
Digenea (Gr. Dis – double, Genos – race) is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms (known as flukes) with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one oral. Adults are particularly common in the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of vertebrates. Once thought to be related to the Monogenea, it is now recognised that they are closest to the Aspidogastrea and that the Monogenea are more closely allied with the Cestoda. Around 6,000 species have been described to date.
Characteristic features of the Digenea include a syncytial tegument; that is, a tegument where the junctions between cells are broken down and a single continuous cytoplasm surrounds the entire animal. A similar tegument is found in other members of the Neodermata; a group of platyhelminths comprising the Digenea, Aspidogastrea, Monogenea and Cestoda. Digeneans possess a vermiform, unsegmented body-plan and have a solid parenchyma with no body cavity (coelom) as in all platyhelminths.
There are typically two suckers, an anterior sucker surrounding the mouth, and a ventral sucker sometimes termed the acetabulum, on the ventral surface. The oral sucker surrounds the mouth, while the ventral sucker is a blind muscular organ with no connection to any internal structure.
...
Wikipedia
