DiPT
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEBI | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
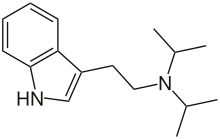
| Formula | C16H24N2 |
| Molar mass | 244.379 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
DiPT /ˈdɪptiː/ or N,N-diisopropyltryptamine /ˌdaɪˌaɪsoʊˌproʊpᵻlˈtrɪptəmiːn/ is a psychedelic hallucinogenic drug of the tryptamine family that has a unique effect. While the majority of hallucinogens affect the visual sense, DiPT is primarily aural. It has been suggested that DiPT may have value to researchers of neurology due to its complex audio distorting effects.
DiPT is a derivative of tryptamine formed by substituting isopropyl groups for the two hydrogen atoms attached to the non-aromatic nitrogen atom in the tryptamine molecule.
Although DiPT's effects are primarily aural, some users have reported that at higher doses they noticed a lack of coordination or balance, confusion, and some users have reported minor visual distortions. Aside from these, the most prevalent non-auditory effect is inner ear pressure (which has been painful in some instances, for example when combined with MDMA). Unlike other psychedelics, users' set and setting doesn't seem to influence what is experienced.
...
Wikipedia
