Darier's disease
| Darier's disease | |
|---|---|
 |
|
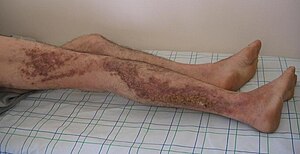
| Linear Darier's disease | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q82.8 (ILDS Q82.868) |
| ICD-9-CM | 757.39 |
| OMIM | 124200 |
| DiseasesDB | 3467 |
| eMedicine | derm/209 |
| MeSH | D007644 |
Darier's disease (DAR), also known as Darier disease, Darier–White disease,Dyskeratosis follicularis and Keratosis follicularis, is an autosomal dominant disorder discovered by French dermatologist Ferdinand-Jean Darier. Darier's is characterized by dark crusty patches on the skin, sometimes containing pus. The crusty patches are also known as keratotic papules, keratosis follicularis or dyskeratosis follicularis.
Mild forms of the disease are the most common, consisting solely of skin rashes that flare-up under certain conditions such as high humidity, high stress or tight-fitting clothes. Even in mild forms, short stature combined with poorly formed fingernails containing vertical striations are diagnostic.
Darier disease affects both men and women and is not contagious. The disease often starts during or later than the teenage years, typically by the third decade. Short stature is common. The symptoms of the disease are thought to be caused by an abnormality in the desmosome-keratin filament complex leading to a breakdown in cell adhesion.
Worldwide prevalence is estimated as between 1: 30,000 and 1: 100,000. Case studies have shown estimated prevalence by country to be 3.8: 100,000 in Slovenia, 1: 36,000 in north-east England, 1: 30,000 in Scotland, and 1: 100,000 in Denmark
It most commonly affects the chest, neck, back, ears, forehead, and groin, but may involve other body areas. The rash associated with Darier's disease often has a distinct odor. Palms & soles may become thickened, intra oral papules can be found. Finger nails become fragile and this helps in diagnosis of the disease. The rash can be aggravated by heat, humidity, and exposure to sunlight. In some cases, sunlight makes it better, especially in the forehead.
Minor forms of the disease are the most common, and may remain undiagnosed throughout life. These consist mainly of minor rashes without odor that are aggravated by heat, humidity, stress and sunlight. Poorly formed fingernails containing vertical striations are diagnostic.
A recent study examined neuropsychiatric conditions in a non-random sample of 100 British individuals assessed as having DAR. There were high lifetime rates for mood disorders (50%), including depression (30%), bipolar disorder (4%), suicidal thoughts (31%) and suicide attempts (13%), suggesting a possible common genetic link. Scattered case studies also suggest a possible link to learning disorders (not yet confirmed).
...
Wikipedia
