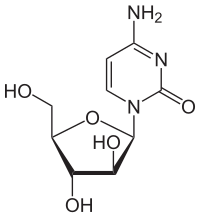
Cytosine arabinoside
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cytosar-U, Depocyt, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682222 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
injectable (intravenous injection or infusion, intrathecal, or subcutaneously) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 20% by mouth |
| Protein binding | 13% |
| Metabolism | liver |
| Biological half-life | biphasic: 10 min, 1–3 hr |
| Excretion | kidney |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.188 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H13N3O5 |
| Molar mass | 243.217 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Cytarabine, also known as cytosine arabinoside (ara-C), is a chemotherapy medication used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is given by injection into a vein, under the skin, or into the cerebrospinal fluid. There is a liposomal formulation for which there is tentative evidence of better outcomes in lymphoma involving the meninges.
Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, vomiting, diarrhea, liver problems, rash, ulcer formation in the mouth, and bleeding. Other serious side effects include loss of consciousness, lung disease, and allergic reactions. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Cytarabine is in the antimetabolite and nucleoside analog families of medication. It works by blocking the function of DNA polymerase.
Cytarabine was patented in 1960 and approved for medical use in 1969. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. The wholesale cost in the developing world is about 4.27 to 5.7 USD per 500 mg vial. This dose in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 50.00 pounds while the liposomal form is 1,223.75 pounds per 50 mg vial.
...
Wikipedia
