Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
di-μ-chlorido-
|
|
| Other names
Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.949 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C16H24Cl2Rh2 | |
| Molar mass | 493.0806 g/mol |
| Density | 1.93 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 243 °C (469 °F; 516 K) |
| Solubility in other solvents | dichloromethane |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
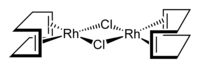
Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer is the organorhodium compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(C8H12)2, commonly abbreviated [RhCl(COD)]2 or Rh2Cl2(COD)2. This yellow-orange, air-stable compound is a widely used precursor to homogeneous catalysts.
The synthesis of [RhCl(COD)]2 involves heating a solution of hydrated rhodium trichloride with 1,5-cyclooctadiene in aqueous ethanol in the presence of sodium carbonate:
[RhCl(COD)]2 is principally used as a source of the electrophile "[Rh(COD)]+."
In this way, chiral phosphines such as chiraphos, DIPAMP, and DIOP have been attached to Rh. The resulting chiral catalysts are capable of asymmetrically hydrogenating certain prochiral alkenes. A closely related but still more reactive complex is chlorobis(cyclooctene)rhodium dimer.
The molecule consists of a pair of square planar Rh centers bound to a 1,5-cyclooctadiene and two chloride ligands that are shared between the Rh centers. The Rh2Cl2 core is also approximately planar, in contrast to the highly bent structure of cyclooctadiene iridium chloride dimer where the dihedral angle is 86°.
...
Wikipedia
