Cryptomonad
| Cryptomonads | |
|---|---|
 |
|
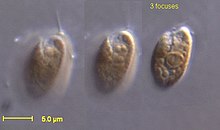
| Rhodomonas salina | |
| Scientific classification (incertae sedis within Eukaryota) | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Phylum: | Cryptophyta Cavalier-Smith, 1986 |
| Class: |
Cryptophyceae West in West & Fritsch, 1927 |
| Typical genera | |
|
Order Cryptomonadales Campylomonas |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Order Cryptomonadales Campylomonas
Chilomonas
Chroomonas
Cryptomonas
Falcomonas
Geminigera
Guillardia
Hemiselmis
Plagioselmis
Proteomonas
Storeatula
Rhodomonas
Teleaulax
Order Goniomonadales
Goniomonas
The cryptomonads (or cryptophytes) are a group of algae, most of which have plastids. They are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella.
Some may exhibit mixotrophy.
Cryptomonads are distinguished by the presence of characteristic extrusomes called ejectisomes or ejectosomes, which consist of two connected spiral ribbons held under tension. If the cells are irritated either by mechanical, chemical or light stress, they discharge, propelling the cell in a zig-zag course away from the disturbance. Large ejectisomes, visible under the light microscope, are associated with the pocket; smaller ones occur underneath the periplast, the cryptophyte-specific cell surrounding.
Cryptomonads have one or two chloroplasts, except for Chilomonas, which has leucoplasts and Goniomonas (formerly Cyathomonas) which lacks plastids entirely. These contain chlorophylls a and c, together with phycobiliproteins and other pigments, and vary in color (brown, red to blueish-green). Each is surrounded by four membranes, and there is a reduced cell nucleus called a nucleomorph between the middle two. This indicates that the plastid was derived from a eukaryotic symbiont, shown by genetic studies to have been a red alga. However, the plastids are very different from red algal plastids: phycobiliproteins are present but only in the thylakoid lumen and are present only as phycoerythrin or phycocyanin. In the case of "Rhodomonas" the crystal structure has been determined to 1.63Å; and it has been shown that the alpha subunit bears no relation to any other known phycobiliprotein.
...
Wikipedia
