Crossbite
| Crossbite | |
|---|---|
 |
|
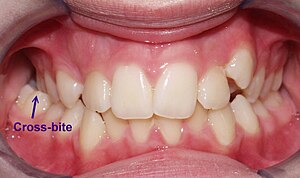
| Unilateral Posterior Crossbite. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | orthodontics |
| ICD-10 | K07.2 |
| ICD-9-CM | 524.27 |
Crossbite is a form of malocclusion where a tooth (or teeth) has a more buccal or lingual position (that is, the tooth is either closer to the cheek or to the tongue) than its corresponding antagonist tooth in the upper or lower dental arch. In other words, crossbite is a lateral misalignment of the dental arches.
An anterior cross bite can be referred as negative overjet, and is typical of class III skeletal relations (prognathism).
An anterior crossbite in a child with baby teeth or mixed dentition may happen due to either dental misalignment or skeletal misalignment. Dental causes may be due to displacement of one or two teeth, where skeletal causes involve either Mandibular hyperplasia, Maxillary hypoplasia or combination of both.
An anterior crossbite due to dental component involves displacement of either maxillary central or lateral incisors lingual to their original erupting positions. This may happen due to delayed eruption of the primary teeth leading to permanent teeth moving lingual to their primary predecessors. This will lead to anterior crossbite where upon biting, upper teeth are behind the lower front teeth and may involve few or all frontal incisors. In this type of crossbite, the maxillary and mandibular proportions are normal to each other and to the cranial base. Another reason that may lead to a dental crossbite is crowding in the maxillary arch. Permanent teeth will tend to erupt lingual to the primary teeth in presence of crowding. Side-effects caused by dental crossbite can be increased recession on the buccal of lower incisors and higher chance of inflammation in the same area. Another term for an anterior crossbite due to dental interferences is Pseudo Class III Crossbite or Malocclusion.
Single tooth crossbites can occur due to uneruption of a primary teeth in a timely manner which causes permanent tooth to erupt in a different eruption pattern which is lingual to the primary tooth. Single tooth crossbites are often fixed by using a finger-spring based appliances. This type of spring can be attached to a removable appliance which is used by patient every day to correct the tooth position.
An anterior crossbite due to skeletal reasons will involve a deficient maxilla and a more hyperplastic or overgrown mandible. People with this type of crossbite will have dental compensation which involves proclined maxillary incisors and retroclined mandibular incisors. A proper diagnosis can be made by having a person bite into their centric relation will show mandibular incisors ahead of the maxillary incisors, which will show the skeletal discrepancy between the two jaws.
...
Wikipedia
