Copaene
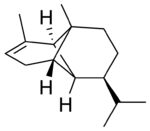 (−)-α-Copaene
|
|
 (−)-β-Copaene
|
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
α: (1R,2S,6S,7S,8S)-8-isopropyl-1,3-dimethyltricyclo[4.4.0.02,7]dec-3-ene
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3856-25-5 (α) 317819-78-6 (β) |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | (α): Interactive image |
| ChemSpider |
10231594 (α) |
| UNII |
0V56HXQ8N5 (α) FDX76373XC (β) |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C15H24 | |
| Molar mass | 204.36 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.939 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 124 °C (255 °F; 397 K) (15 mmHg) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Copaene, or more precisely, α-copaene, is the common (or trivial) chemical name of an oily liquid hydrocarbon that is found in a number of essential oil-producing plants. The name is derived from that of the resin-producing tropical copaiba tree, Copaifera langsdorfii, from which the compound was first isolated in 1914. Its structure, including the chirality, was determined in 1963. The double-bond isomer with an exo-methylene group, β-copaene, was first reported in 1967.
Chemically, the copaenes are tricyclic sesquiterpenes. The molecules are chiral, and the α-copaene enantiomer most commonly found in higher plants exhibits a negative optical rotation of about −6°. The rare (+)-α-copaene is also found in small amounts in some plants. It is of economic significance because it is strongly attracting to an agricultural pest, the Mediterranean fruit fly Ceratitis capitata.
...
Wikipedia
