Congenital cytomegalovirus infection
| Congenital cytomegalovirus infection | |
|---|---|
 |
|
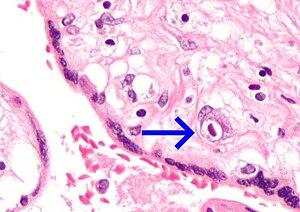
| Micrograph of a cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection of the placenta (CMV placentitis). The characteristic large nucleus of a CMV infected cell is seen off-centre at the bottom-right of the image. H&E stain | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | pediatrics |
| ICD-10 | P35.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 771.1 |
| MedlinePlus | 001343 |
| eMedicine | article/963090 |
Congenital cytomegalovirus infection refers to a condition where cytomegalovirus is transmitted in the prenatal period.
Human cytomegalovirus is one of the vertically transmitted infections that lead to congenital abnormalities. (Others are: toxoplasmosis, rubella, and herpes simplex. )
Congenital HCMV infection occurs when the mother suffers a primary infection (or reactivation) during pregnancy. Due to the lower seroprevalence of HCMV in industrialized countries and higher socioeconomic groups, congenital infections are actually less common in poorer communities, where more women of child-bearing age are already seropositive. In industrialized countries up to 8% of HCMV seronegative mothers contract primary HCMV infection during pregnancy, of which roughly 50% will transmit to the fetus. Between 22–38% of infected fetuses are then born with symptoms, which may include pneumonia, gastrointestinal, retinal and neurological disease. HCMV infection occurs in roughly 1% of all neonates with those who are not congenitally infected contracting the infection possibly through breast milk. Other sources of neonatal infection are bodily fluids which are known to contain high titres in shedding individuals: saliva (<107copies/ml) and urine (<105copies/ml ) seem common routes of transmission.
The incidence of primary CMV infection in pregnant women in the United States varies from 1% to 3%. Healthy pregnant women are not at special risk for disease from CMV infection. When infected with CMV, most women have no symptoms and very few have a disease resembling infectious mononucleosis. It is their developing fetuses that may be at risk for congenital CMV disease. CMV remains the most important cause of congenital viral infection in the United States. HCMV is the most common cause of congenital infection in humans and intrauterine primary infections are more common than other well-known infections and syndromes, including Down Syndrome, Fetal Alcohol Syndrome, Spina Bifida, and Pediatric HIV/AIDS.
For infants who are infected by their mothers before birth, two potential adverse scenarios exist:
These risks appear to be almost exclusively associated with women who previously have not been infected with CMV and who are having their first infection with the virus during pregnancy. There appears to be little risk of CMV-related complications for women who have been infected at least 6 months prior to conception. For this group, which makes up 50% to 80% of the women of child-bearing age, the rate of newborn CMV infection is 1%, and these infants appear to have no significant illness or abnormalities.
...
Wikipedia
