Congenital cataract
| Congenital cataract | |
|---|---|
 |
|
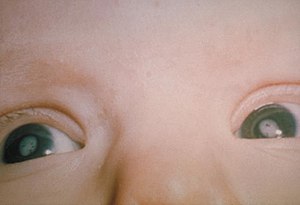
| Bilateral cataracts in an infant due to congenital rubella syndrome. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q12.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 743.3 |
| MedlinePlus | 001615 |
The term congenital cataract refers to a lens opacity present at birth. Congenital cataracts cover a broad spectrum of severity: whereas some lens opacities do not progress and are visually insignificant, others can produce profound visual impairment.
Congenital cataracts may be unilateral or bilateral. They can be classified by morphology, presumed or defined genetic etiology, presence of specific metabolic disorders, or associated ocular anomalies or systemic findings.
Congenital cataracts occur in a variety of morphologic configurations, including lamellar, polar, sutural, coronary, cerulean, nuclear, capsular, complete, membranous.
In general, approximately one-third of congenital cataracts are a component of a more extensive syndrome or disease (e.g., cataract resulting from congenital rubella syndrome), one-third occur as an isolated inherited trait, and one-third result from undetermined causes. Metabolic diseases tend to be more commonly associated with bilateral cataracts.
Other (Coxsackievirus, Syphilis, Varicella-Zoster, HIV, and Parvo B19)
...
Wikipedia
