Colville River (Alaska)
| Colville River | |
|
Inupiat family on Colville River, 1901.
|
|
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| State | Alaska |
| Borough | North Slope |
| Source | Confluence of Thunder and Storm creeks |
| - location | North slope of the De Long Mountains |
| - elevation | 2,017 ft (615 m) |
| - coordinates | 68°49′01″N 160°21′14″W / 68.81694°N 160.35389°W |
| Mouth | Harrison Bay, Beaufort Sea, Arctic Ocean |
| - location | Northeast of Nuiqsut |
| - elevation | 0 ft (0 m) |
| - coordinates | 70°26′46″N 150°21′28″W / 70.44611°N 150.35778°WCoordinates: 70°26′46″N 150°21′28″W / 70.44611°N 150.35778°W |
| Length | 350 mi (563 km) |
| Basin | 20,500 sq mi (53,000 km2) |
|
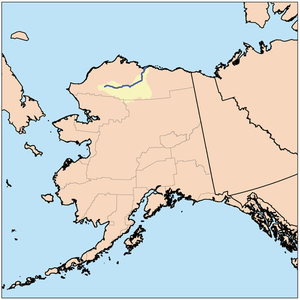
Colville River course and drainage basin in northern Alaska.
|
|
The Colville River (Inupiat: Kuukpik) is a major river of the Arctic Ocean coast of Alaska in the United States, approximately 350 miles (560 km) long. One of the northernmost major rivers in North America, it drains a remote area of tundra on the north side of the Brooks Range entirely above the Arctic Circle. The river is frozen for more than half the year and floods each spring.
It rises on the north slope of the De Long Mountains, at the western end of the Brooks Range, north of the continental divide in the southwestern corner of the National Petroleum Reserve. It flows initially north, then generally east through the foothills on the north side of the range, broadening as it receives the inflow of many tributaries that descend from the middle Brooks Range. Along its middle course it forms the southeastern border of the National Petroleum Reserve. At the Iñupiat village of Umiat it turns north to flow across the Arctic plain, entering the western Beaufort Sea in a broad delta near Nuiqsut, approximately 120 mi (190 km) west of Prudhoe Bay.
Measuring about 20 by 23 by 26 miles (32 by 37 by 42 km), the river's triangular delta includes 34 distributaries, each with its own mouth, at normal water stages. During high water, the number of distributaries may reach 5,000. The largest distributary is the Nechalic Channel, which flows through Nuiqsut.
The river valley contains unexploited petroleum and natural gas deposits. A current proposal by the State of Alaska to bridge the river near Nuiqsut would be the first major river crossing north of the Arctic Circle in North America.
...
Wikipedia