Colistin sulfate
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Coly-mycinm; Coly-monas (India) |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
topical, oral, intravenous, inhaled |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 0% |
| Biological half-life | 5 hours |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.668 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
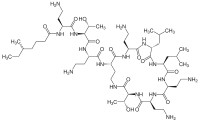
| Formula | C52H98N16O13 |
| Molar mass | 1155.4495 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Colistin, also known as polymyxin E, is an antibiotic produced by certain strains of the bacteria Paenibacillus polymyxa. Colistin is a mixture of the cyclic polypeptides colistin A and B and belongs to the class of polypeptide antibiotics known as polymyxins. Colistin is effective against most Gram-negative bacilli.
Colistin is a decades-old drug that fell out of favor in human medicine due to its kidney toxicity. It remains one of the last-resort antibiotics for multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Acinetobacter.NDM-1 metallo-β-lactamase multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae have also shown susceptibility to colistin.
Resistance to colistin in humans is rare. The first colistin-resistance gene in a plasmid which can be transferred between bacterial strains was found in 2011 in China and became publicly known in November 2015. The presence of this plasmid-borne mcr-1 gene was confirmed starting December 2015 in SE-Asia, several European countries and the United States.
Colistin was first isolated in Japan in 1949 from a flask of fermenting Bacillus polymyxa var. colistinus by the Japanese scientist Koyama and became available for clinical use in 1959
Colistimethate sodium, a less toxic prodrug, became available for injection in 1959. In the 1980s, polymyxin use was widely discontinued because of nephro- and neurotoxicity. As multi-drug resistant bacteria became more prevalent in the 1990s, colistin started to get a second look as an emergency solution, in spite of toxic effects.
Two forms of colistin are available commercially: colistin sulfate and colistimethate sodium (colistin methanesulfonate sodium, colistin sulfomethate sodium). Colistin sulfate is cationic; colistimethate sodium is anionic. Colistin sulfate is stable, but colistimethate sodium is readily hydrolysed to a variety of methanesulfonated derivatives. Colistin sulfate and colistimethate sodium are eliminated from the body by different routes. With respect to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, colistimethate is the inactive prodrug of colistin. The two drugs are not interchangeable .
...
Wikipedia
