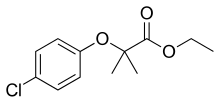
Clofibrate
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | Variable, 92–97% at therapeutic concentrations |
| Metabolism | Hydrolyzed to clofibric acid; hepatic glucuronidation |
| Biological half-life | Highly variable; average 18–22 hours. Prolonged in renal failure |
| Excretion | Renal, 95 to 99% |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.253 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H15ClO3 |
| Molar mass | 242.698 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Boiling point | 148 °C (298 °F) |
|
|
|
|
Clofibrate (tradename Atromid-S) is an organic compound. It is marketed as a fibrate. It is a lipid-lowering agent used for controlling the high cholesterol and triacylglyceride level in the blood. It increases lipoprotein lipase activity to promote the conversion of VLDL to LDL, and hence reduce the level of VLDL. It can increase the level of HDL as well.
It can induce SIADH, syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone ADH (vasopressin). Clofibrate can also result in formation of cholesterol stones in the gallbladder.
The World Health Organization Cooperative Trial on Primary Prevention of Ischaemic Heart Disease using clofibrate to lower serum cholesterol observed excess mortality in the clofibrate-treated group despite successful cholesterol lowering (47% more deaths during treatment with clofibrate and 5% after treatment with clofibrate) than the non-treated high cholesterol group. These deaths were due to a wide variety of causes other than heart disease, and remain "unexplained".
Clofibrate was discontinued in 2002 due to adverse effects.
...
Wikipedia
