Cas9
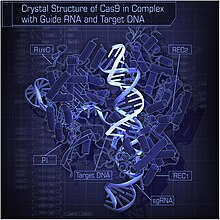
Crystal structure of S pyogenes Cas9 in complex with guide RNA and its target DNA at 2.5 A ˚ resolution.(Nishimasu, et al. 2014)
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Organism | |
| Symbol | cas9 |
| Alt. symbols | SPy_1046 |
| RefSeq (Prot) | NP_269215.1 |
| UniProt | Q99ZW2 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 3.1.-.- |
| Chromosome | genomic: 0.85 - 0.86 Mb |
Cas9 (CRISPR associated protein 9) is an RNA-guided DNA endonuclease associated with the CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) type II adaptive immunity system in , among other bacteria. S. pyogenes utilizes Cas9 to interrogate and cleave foreign DNA, such as invading bacteriophage DNA or plasmid DNA. Cas9 performs this interrogation by unwinding foreign DNA and checking whether it is complementary to the 20 basepair spacer region of the guide RNA. If the DNA substrate is complementary to the guide RNA, Cas9 cleaves the invading DNA. In this sense, the CRISPR-Cas9 mechanism has a number of parallels with the RNA interference (RNAi) mechanism in eukaryotes. Native Cas9 assists in all three CRISPR steps: it participates in adaptation, participates in crRNA processing and it cleaves the target DNA assisted by crRNA and an additional RNA called tracrRNA. Native Cas9 requires a guide RNA composed of two disparate RNAs that associate to make the guide - the CRISPR RNA (crRNA), and the trans-activating RNA (tracrRNA).,
The Cas9 protein has been heavily utilized as a genome engineering tool to induce site-directed double strand breaks in DNA. These breaks can lead to gene inactivation or the introduction of heterologous genes through non-homologous end joining and homologous recombination respectively in many laboratory model organisms. Alongside zinc finger nucleases and TALEN proteins, Cas9 is becoming a prominent tool in the field of genome editing. Cas9 has gained traction in recent years because it can cleave nearly any sequence complementary to the guide RNA. Because the target specificity of Cas9 stems from the guide RNA:DNA complementarity and not modifications to the protein itself (like TALENs and Zinc-fingers), engineering Cas9 to target new DNA is straightforward. Versions of Cas9 that bind but do not cleave cognate DNA can be used to localize transcriptional activator or repressors to specific DNA sequences in order to control transcriptional activation and repression. Cas9 targeting has been simplified through the engineering of a chimeric single guide RNA. Scientists have suggested that Cas9-based gene drives may be capable of editing the genomes of entire populations of organisms. In 2015, scientists in China used Cas9 to modify the genome of human embryos for the first time.
...
Wikipedia
