Cardio-surgery
| Cardiac surgery | |
|---|---|
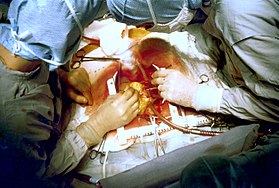
Two cardiac surgeons performing coronary artery bypass surgery. Note the use of a steel retractor to forcefully maintain the exposure of the heart.
|
|
| ICD-9-CM | 35-37 |
| MeSH | D006348 |
| OPS-301 code | 5-35...5-37 |
Cardiac surgery, or cardiovascular surgery, is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. It is often used to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, with coronary artery bypass grafting); to correct congenital heart disease; or to treat valvular heart disease from various causes, including endocarditis, rheumatic heart disease, and atherosclerosis. It also includes heart transplantation.
The earliest operations on the pericardium (the sac that surrounds the heart) took place in the 19th century and were performed by Francisco Romero (1801),Dominique Jean Larrey (1810), Henry Dalton (1891), and Daniel Hale Williams (1893). The first surgery on the heart itself was performed by Axel Cappelen on 4 September 1895 at Rikshospitalet in Kristiania, now Oslo. Cappelen ligated a bleeding coronary artery in a 24-year-old man who had been stabbed in the left axilla and was in deep shock upon arrival. Access was through a left thoracotomy. The patient awoke and seemed fine for 24 hours, but became ill with a fever and died three days after the surgery from mediastinitis.
...
Wikipedia
