Carbohydrazide
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
1,3-Diaminourea
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
497-18-7 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) |
Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:61308 |
| ChemSpider |
66578 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.126 |
| PubChem | 73948 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| CH6N4O | |
| Molar mass | 90.09 g/mol |
| Density | 1.341 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 153 to 154 °C (307 to 309 °F; 426 to 427 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
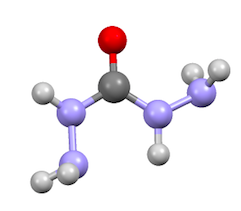
Carbohydrazide is the chemical compound with the formula OC(N2H3)2. It is a white, water-soluble solid. It decomposes upon melting. A number of carbazides are known where one or more N-H groups are replaced by other substituents. They occur widely in the drugs, herbicides, plant growth regulators, and dyestuffs.
Industrially the compound is produced by treatment of urea with hydrazine:
It can also be prepared by reactions of other C1-precursors with hydrazine, such as carbonate esters. It can be prepared from phosgene, but this route cogenerates the hydrazinium salt [N2H5]Cl and results in some diformylation. Carbazic acid is also a suitable precursor:
The molecule is nonplanar. All nitrogen centers are at least somewhat pyramidal, indicative of weaker C-N pi-bonding. The C-N and C-O distances are about 1.36 and 1.25 Å, respectively.
Heating carbohydrazide may result in an explosion. Carbohydrazide is harmful if swallowed, irritating to eyes, respiratory system, and skin. Carbohydrazide is toxic to aquatic organisms.
...
Wikipedia
