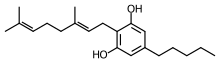
Cannabigerol
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H32O2 |
| Molar mass | 316.49 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cannabigerol (CBG) is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid found in the Cannabis genus of plants. CBG is the non-acidic form of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), the parent molecule (“mother cannabinoid”) from which many other cannabinoids are made. By the time most strains of cannabis reach maturity, most of the CBG has been converted into other cannabinoids, primarily tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or cannabidiol (CBD), usually leaving somewhere below 1% CBG in the plant.
CBG has been found to act as a high affinity α2-adrenergic receptor agonist, moderate affinity 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, and low affinity CB1 receptor antagonist. It also binds to the CB2 receptor as an antagonist. CBG does not trigger THC-like activity in mice, rats, gerbils and non-human primates, consistent with it being non-intoxicating. Moreover, CBG was without effect up to 80 mg/kg in the mouse tetrad test of cannabimimetic activity (locomotor suppression, catalepsy, hypothermia and analgesia).
It has two E/Z isomers.
CBG has potential for alleviating pain, especially neuropathic pain where tests suggest a higher efficacy than CBD CBG can also inhibit the uptake of GABA in the brain, which can decrease anxiety and muscle tension with tests on mice showing that CBG induces antidepressant effects similar to imipramine.
It has been shown to improve a model of inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
CBG induces production of the body’s natural skin moisturizers, holding promise for dry-skin syndromes and with the potential to treat other skin conditions.
...
Wikipedia
