CS gas
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
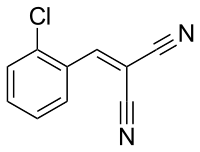
Preferred IUPAC name
[(2-Chlorophenyl)methylidene]propanedinitrile
|
|
| Other names
2-(2-Chlorobenzylidene)malononitrile
2-Chlorobenzalmalononitrile o-Chlorobenzylidene malononitrile OCBM Tear gas |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
2698-41-1 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider |
16644 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.435 |
| 4158 | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H5Cl N2 | |
| Molar mass | 188.6 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder Colourless gas when burned |
| Odor | pepper-like |
| Density | 1.04 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 93 °C (199 °F; 366 K) |
| Boiling point | 310 °C (590 °F; 583 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Vapor pressure | (mm Hg) 3.4 × 10−5 at 20 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | See: data page |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LCLo (lowest published)
|
1806 mg/m3 (rat, 45 min) 2753 mg/m3 (mouse, 20 min) 1802 mg/m3 (rabbit, 10 min) 2326 mg/m3 (guinea pig, 10 min) |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.05 ppm (0.4 mg/m3) |
|
REL (Recommended)
|
C 0.05 ppm (0.4 mg/m3) [skin] |
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
2 mg/m3 |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
SDBS
5-chloro-2-quinolinecarbonitrile |
| Supplementary data page | |
|
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
5-chloro-2-quinolinecarbonitrile
6-chloro-2-quinolinecarbonitrile
7-chloro-2-quinolinecarbonitrile
The compound 2-chlorobenzalmalononitrile (also called o-chlorobenzylidene malononitrile) (chemical formula: C10H5ClN2), a cyanocarbon, is the defining component of a tear gas commonly referred to as CS gas, which is used as a riot control agent. Exposure causes a burning sensation and tearing of the eyes to the extent that the subject cannot keep their eyes open, and a burning irritation of the nose, mouth and throat mucous membranes causing profuse coughing, mucous nasal discharge, disorientation, and difficulty breathing, partially incapacitating the subject. CS gas is an aerosol of a volatile solvent (a substance that dissolves other active substances and that easily evaporates) and 2-chlorobenzalmalononitrile, which is a solid compound at room temperature. CS gas is generally accepted as being non-lethal. It was first synthesized by two Americans, Ben Corson and Roger Stoughton, at Middlebury College in 1928, and the chemical's name is derived from the first letters of the scientists' surnames.
CS was developed and tested secretly at Porton Down in Wiltshire, England, in the 1950s and 1960s. CS was used first on animals, then subsequently on British Army servicemen volunteers. CS has less effect on animals due to "under-developed tear-ducts and protection by fur".
CS is synthesized by the reaction of 2-chlorobenzaldehyde and malononitrile via the Knoevenagel condensation:
The reaction is catalysed with weak base like piperidine or pyridine. The production method has not changed since the substance was discovered by Corson and Stoughton. Other bases, solvent free methods and microwave promotion have been suggested to improve the production of the substance.
...
Wikipedia

